Logical Devices Introduction
Logical devices enable you to plan your network fabric before selecting underlying hardware. By abstracting specific vendors and models you can design based on a common set of form factors like ports, speeds and roles. Some applications of logical devices include:
- Specifying speed and roles for specific ports (For example, the 48th port is always a leaf, or the speed of the 10th port is always 1 Gbps).
- Preparing for port speed transformations (For example, transforming one - 40 GbE port into four - 10 GbE ports).
- Using non-standard port speeds (For example, for a 1 GbE SFP in a 10 GbE port, the underlying hardware is automatically configured correctly.)
- Solving for automatic cable map generation that takes into account failure domains on modular systems (for example, a line card).
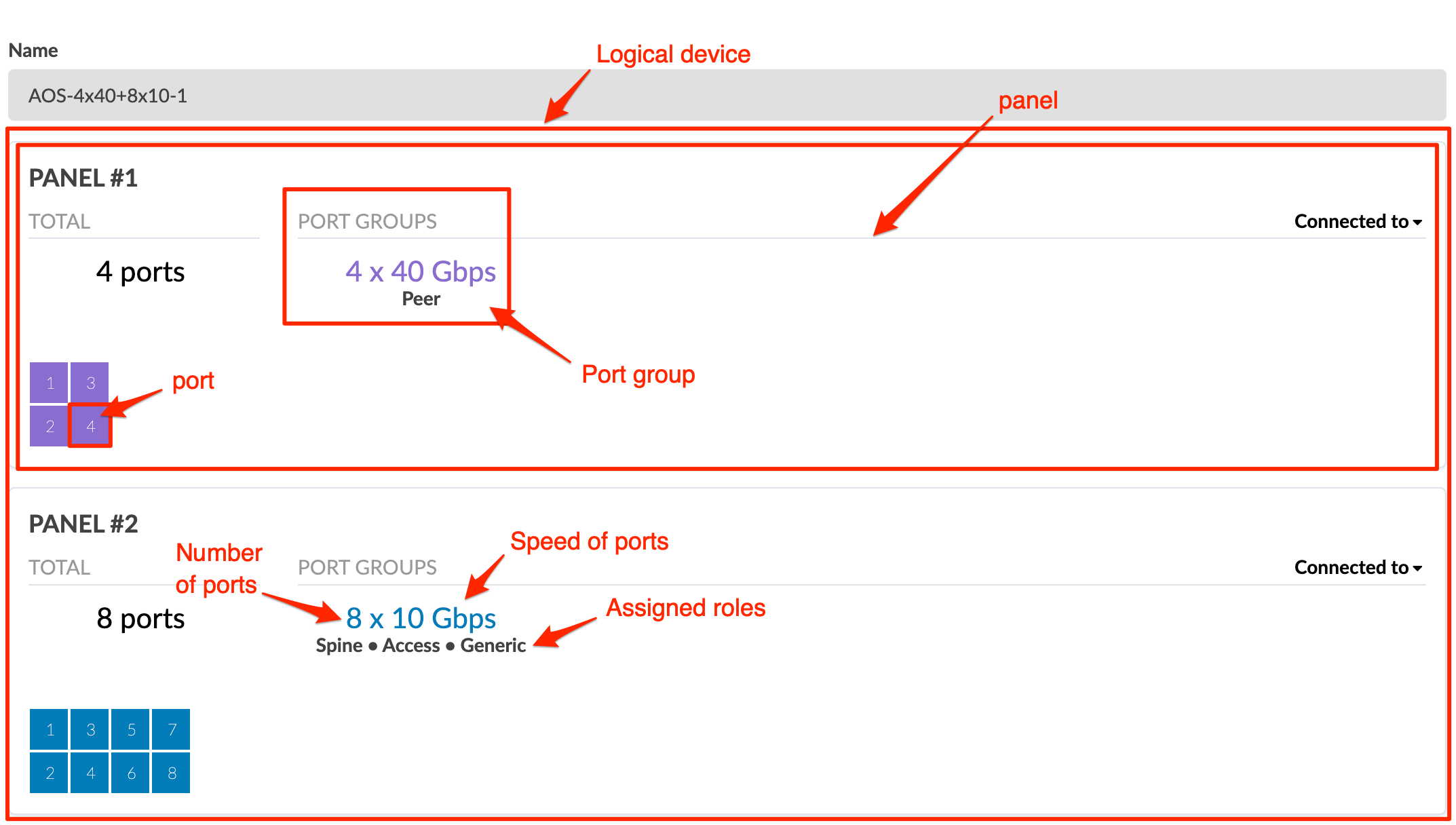
Logical devices include the following details:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Logical device name | A unique name to identify the logical device, 64 characters or fewer |
| Panel | Port layout based on IP fabric, forwarding engine, line card (slot) or physical layout. A panel contains one or more port groups. A logical device includes one or more panels. |
| Port Group | A collection of ports with the same speed and role(s) |
| Number of ports | Number of ports in the port group |
| Speed | Speed of ports in the port group |
| Roles | Ports are configured to face the following types of devices:
|
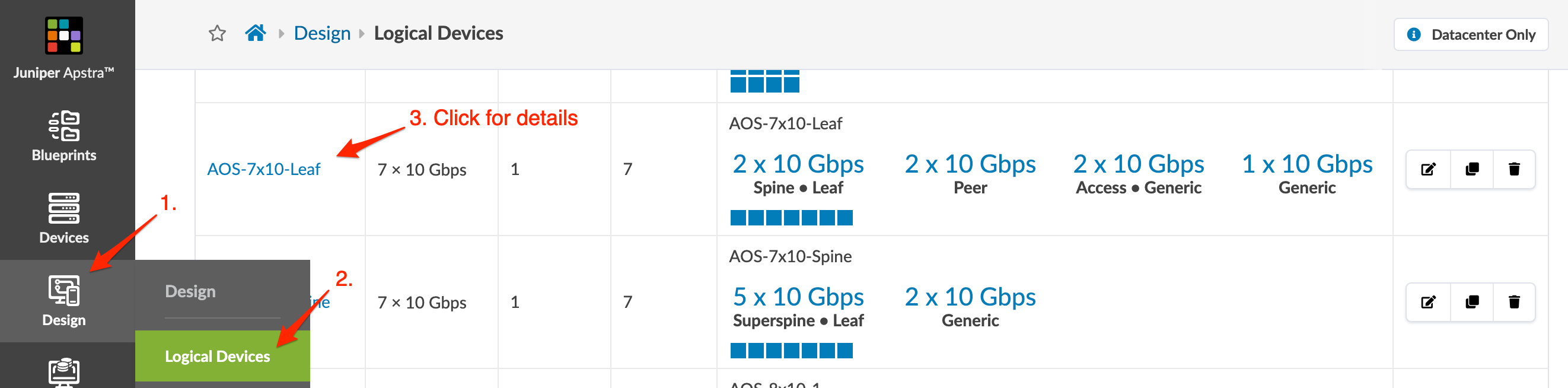
From the left navigation menu, navigate to Design > Logical Devices to go to logical devices in the global catalog. Apstra ships with many predefined logical devices. Click a logical device name in the table to see its details. For our example, we'll use a logical device consisting of 7 ports with varying roles.
Logical devices are mapped to device profiles (specific vendor models) and they're used in rack types and rack-based templates.
