Syslog Configuration (Platform)
Syslog Overview
System Log (syslog) is a running list of everything that's going on in your system. You can use these logs to audit events or review anomalies. You can configure syslog to send messages for specific types of systems (facilities) to external syslog servers. (You can also export event logs to a CSV file.)
Syslog configuration includes the following details:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
IP Address |
The remote syslog server IP address or hostname |
|
Port |
The remote syslog server port |
|
Protocol |
UDP or TCP |
|
Facility |
The type of system that's logging the messages Facilities are mapped to Apstra syslogs as follows:
|
| Time Zone | The syslog message time zone. If you have proper time zone translation, you won't need to synch the system time zone (or Docker time zone) with your external syslog server. Rather than assuming the message time is in Zulu/UTC-0, the time zone translation needs to append the correct time zone information to the timestamp. Then, you can better correlate Apstra events in your external message systems. |
Syslog messages follow Common Event Format (CEF) conventions as shown below:
{host} is the the Apstra server hostname. If you want to change the hostname, you must use the procedure on the Change Apstra Server Hostname page. If you change the hostname with any other method, the new hostname won't be included in syslog entries.
AOS Log Format:
'{timestamp} {host}'
'CEF:{version}|{device_vendor}|{device_product}|{device_version}|'
'{device_event_class_id}|{name}|{severity}|{extension}
Where:
{version} : CEF version, currently always "0"
{device_vendor} : always "Apstra"
{device_product} : always "AOS"
{device_version} : current AOS version
{device_event_class_id} : "100" for audit logs, "101" for anomaly logs
{name} : "Audit event" for audit logs, "Alert" for anomaly logs
{severity} : "5" for audit logs, "10" for anomaly logs
And where {extension} is either :
For anomaly logs : msg=<json payload>
For audit logs : cat=<activity> src=<src_IP> suser=<username> act=<activity result> cs1Label=<field1_type> cs1=<field1_value> cs2Label=<field2_type> cs2=<field2_value> cs3Label=<field3_type> cs3=<field3_value>
Anomaly Log JSON Format
blueprint_label : Name of the blueprint the anomaly was raised in.
timestamp : Unix timestamp when the Anomaly was raised.
origin_name : Serial Number of the device the anomaly affects.
alert : The value is a JSON Payload with the actual anomaly (see Alert JSON Payload below)
origin_hostname : Hostname of the device the anomaly affects. It can be AOSHOST, an empty string if the hostname could not be determined or a valid value.
device_hostname : Hostname of the device the anomaly affects or <device hostname unknown> if a hostname could not be determined
origin_role : Role of the device the anomaly affects.
Alert JSON Payload:
<ALERT TYPE>_alert: Contains a JSON payload with key-value pair of information pertaining to the alert. Here <ALERT TYPE>_alert can be valid anomaly/alert names such as hostname_alert, probe_alert, liveness_alert etc.
id : UUID of the anomaly.
first_seen : Unix timestamp when the Anomaly was raised for the first time.
raised : True when anomaly is present, False when it is cleared.
severity : The severity level of the anomaly. Set to 3 for critical, 2 for high, 1 for medium and 0 for low.
Audit Log Format:
cat : Activity performed. Valid values: "Login", "Logout","BlueprintCommit","BlueprintRevert","BlueprintRollback", "BlueprintDelete","DeviceConfigChange",
"OperationModeChangeToMaintenance","OperationModeChangeToNormal","OperationModeChangeToReadOnly","RatelimitExceptionAdd","RatelimitExceptionDelete",
"RatelimitClear","SystemChangeApiOperationModeToMaintenance","SystemChangeApiOperationModeToNormal","UserCrete","UserUpdate","UserDelete",
"SyslogCreate","SyslogUpdate","SyslogDelete","AuthAclEnable","AuthAclDisable","AuthAclRuleAdd","AuthAclRuleUpdate" and "AuthAclRuleDelete".
src : Source IP of the client making HTTP requests to perform the activity.
suser : Who performed the activity.
act : Outcome of the activity - free-form string. In the case when the activity was performed successfully, the value stored is “Success“. In case of error, include error string. Ex: Unauthorized
cs1Label : The string “Blueprint Name”. Only exists if activity is associated with a blueprint (optional)
cs1 : Name of the blueprint on which action was taken. Only exists if activity is associated with a blueprint (optional)
cs2Label : The string “Blueprint ID”. Only exists if activity is associated with a blueprint (optional)
cs2 : Id of the blueprint on which action was taken. Only exists if activity is associated with a blueprint (optional)
cs3Label : The string “Commit Message”. Only exists if user has added a commit message (optional)
cs3 : Commit Message. Only exists if user has added a commit message (optional)
deviceExternalId : Id (typically serial number) of the managed device on which action was taken. Only exists if activity is associated with a device such as for “DeviceConfigChange” (optional)
deviceConfig : Config that is pushed and applied on the device where “#012” is used to indicate a line break to log collectors and parsers. Only exists if activity is associated with a device such as for “DeviceConfigChange” (optional)Example of Audit Syslog Message:
Jan 31 03:11:01 aos-server - 2023-01-31T03:11:01.699190+0000 aos-server CEF:0|Apstra|AOS|4.1.2-269|100|Audit event|5|cat=Logout src=172.24.212.62 suser=admin act=Success Jan 31 03:11:01 aos-server - 2023-01-31T03:11:01.699190+0000 aos-server CEF:0|Apstra|AOS|4.1.2-269|100|Audit event|5|cat=BlueprintCommit src=172.24.212.62 suser=admin act=Success cs1Label=Blueprint Name cs1=rack-based-blueprint-33ded50f cs2Label=Blueprint ID cs2=rack-based-blueprint-33ded50f
Example of Anomaly Syslog Message:
Jan 31 03:11:01 aos-server - 2023-01-31T03:11:01.699190+0000 aos-server
CEF:0|Apstra|AOS|4.1.2-269|101|Alert|10|msg={u'blueprint_label': u'rack-based-blueprint-33ded50f', u'timestamp': 1679002758562407, u'origin_name':
u'time_series', u'alert': {u'probe_alert': {u'expected_int_max': 99, u'stage_name': u'leaf_match_perc_range', u'probe_label': u'leaf_to_spine_interface_statuses',
u'actual_int': 83, u'probe_id': u'60b03bb0-0e22-4a6d-b32d-e15085149b7b', u'key_value_pairs': [], u'item_id': u'1', u'expected_int': -9223372036854775808},
u'first_seen': 1679002758562121, u'raised': False, u'severity': 3, u'id': u'02a17b60-cc3e-4afb-baba-733a8c654df6'}, u'origin_hostname': u'AOSHOST',
'device_hostname': '<device hostname unknown>', u'origin_role': u''}
Jan 31 03:11:01 aos-server - 2023-01-31T03:11:01.699190+0000 aos-server
CEF:0|Apstra|AOS|4.1.2-269|101|Alert|10|msg={u'blueprint_label': u'rack-based-blueprint-33ded50f', u'timestamp': 1679002754682990, u'origin_name':
u'50540015FA9D', u'alert': {u'first_seen': 1679002749600167, u'raised': False, u'severity': 3, u'hostname_alert': {u'expected_hostname': u'leaf-3',
u'actual_hostname': u''}, u'id': u'0457a759-7d3a-4bf8-97e8-e13e518cf267'}, u'origin_hostname': u'', 'device_hostname': '<device hostname unknown>', u'origin_role': u'leaf'}From the left navigation menu, navigate to Platform > External Services
> Syslog Configuration to see configurations. You can create,
clone, edit and delete syslog configurations. 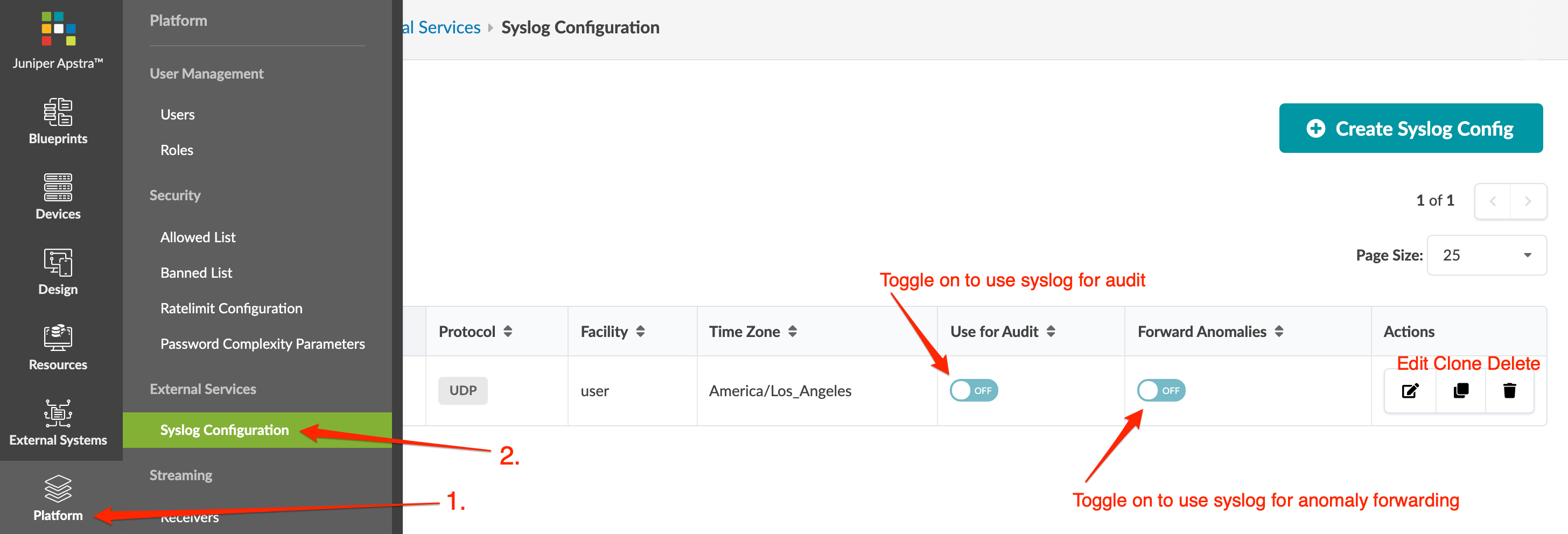
Create Syslog Config
- From the left navigation menu, navigate to Platform > External Services > Syslog Configuration and click Create Syslog Config (top-right).
- Configure the Syslog server. (See overview above for details.)
- Click Create to save the configuration and return to the table view.
- To configure another Syslog server, repeat the steps above.
- To enable messages to be sent to a configured server, toggle on Use for Audit and/or Forward Anomalies, as appropriate.
Edit Syslog Config
- From the left navigation menu, navigate to Platform > External Services > Syslog Configuration and click the Edit button for the Syslog configuration to edit.
- Make your changes.
- Click Update to update the Syslog configuration and return to the table view.
Delete Syslog Config
- From the left navigation menu, navigate to Platform > External Services > Syslog Configuration and click the Delete button for the Syslog configuration to delete.
- Click Delete Syslog Config to delete the Syslog configuration and return to the table view.
